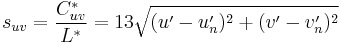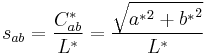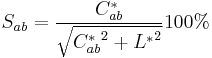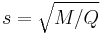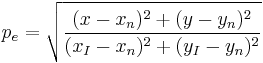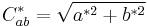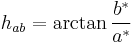Colorfulness
In colorimetry and color theory, colorfulness, chroma, and saturation are related but distinct concepts referring to the perceived intensity of a specific color. Colorfulness is the degree of difference between a color and gray. Chroma is the colorfulness relative to the brightness of another color that appears white under similar viewing conditions. Saturation is the colorfulness of a color relative to its own brightness.[1] Though this general concept is intuitive, terms such as chroma, saturation, purity, and intensity are often used without great precision, and even when well-defined depend greatly on the specific color model in use.
A highly colorful stimulus is vivid and intense, while a less colorful stimulus appears more muted, closer to gray. With no colorfulness at all, a color is a “neutral” gray (an image with no colorfulness in any of its colors is called grayscale). With three attributes—colorfulness (or chroma or saturation), lightness (or brightness), and hue—any color can be described.
Contents |
Saturation
Saturation is one of three coordinates in the HSL and HSV color spaces. Note that virtually all computer software implementing these spaces use a very rough approximation to calculate the value they call "saturation", such as the formula described for HSV and this value has little, if anything, to do with the description shown here.
The saturation of a color is determined by a combination of light intensity and how much it is distributed across the spectrum of different wavelengths. The purest (most saturated) color is achieved by using just one wavelength at a high intensity, such as in laser light. If the intensity drops, then as a result the saturation drops. To desaturate a color of given intensity in a subtractive system (such as watercolor), one can add white, black, gray, or the hue's complement.
Various correlates of saturation follow.
- CIELUV
- The chroma normalized by the lightness:
where (u′n, v′n) is the chromaticity of the white point, and chroma is defined below.[2]
By analogy, in CIELAB this would yield:
The CIE has not formally recommended this equation since CIELAB has no chromaticity diagram, and this definition therefore lacks direct correlation with older concepts of saturation.[3] Nevertheless, this equation provides a reasonable predictor of saturation, and demonstrates that adjusting the lightness in CIELAB while holding (a*, b*) fixed does affect the saturation.
But the following formula is in agreement with the human perception of saturation: The formula proposed by Eva Lübbe is in agreement with the verbal definition of Manfred Richter: Saturation is the proportion of pure chromatic color in the total color sensation.[4]
where Sab is the saturation, L* the lightness and C*ab is the chroma of the color.
- CIECAM02
- The square root of the colorfulness divided by the brightness:
This definition is inspired by experimental work done with the intention of remedying CIECAM97s's poor performance.[5][6] M is proportional to the chroma C (M = CFL0.25), thus the CIECAM02 definition bears some similarity to the CIELUV definition. An important difference is that the CIECAM02 model accounts for the viewing conditions through the parameter FL.[5]
Excitation purity
The excitation purity (purity for short) of a stimulus is its difference from the illuminant's white point relative to the furthest point on the chromaticity diagram with the same hue (dominant wavelength for monochromatic sources); using the CIE 1931 color space:[7]
where (xn, yn) is the chromaticity of the white point and (xI, yI) is the point on the perimeter whose line segment to the white point contains the chromaticity of the stimulus. Different color spaces, such as CIELAB or CIELUV may be used, and will yield different results.
Chroma in CIE 1976 L*a*b* and L*u*v* color spaces
The naïve definition of saturation does not specify its response function. In the CIE XYZ and RGB color spaces, the saturation is defined in terms of additive color mixing, and has the property of being proportional to any scaling centered at white or the white point illuminant. However, both color spaces are nonlinear in terms of psychovisually perceived color differences. It is also possible, and sometimes desirable to define a saturation-like quantity that is linearized in term of the psychovisual perception.
In the CIE 1976 L*a*b* and L*u*v* color spaces, the unnormalized chroma is the radial component of the cylindrical coordinate CIE L*C*h (lightness, chroma, hue) representation of the L*a*b* and L*u*v* color spaces, also denoted as CIE L*C*h(a*b*) or CIE L*C*h for short, and CIE L*C*h(u*v*). The transformation of (a*, b*) to (C*ab, hab) is given by:
and analogously for CIE L*C*h(u*v*).
The chroma in the CIE L*C*h(a*b*) and CIE L*C*h(u*v*) coordinates has the advantage of being more psychovisually linear, yet they are non-linear in terms of linear component color mixing. And therefore, chroma in CIE 1976 L*a*b* and L*u*v* color spaces is very much different from the traditional sense of "saturation".
Chroma in color appearance models
Another, psychovisually even more accurate, but also more complex method to obtain or specify the saturation is to use the color appearance model, like CIECAM. The chroma component of the LCh (lightness, chroma, hue) coordinate, and becomes a function of parameters like the chrominance and physical brightness of the illumination, or the characteristics of the emitting/reflecting surface, which is also psychovisually more sensible.
References
- ^ Mark D. Fairchild. “Color Appearance Models: CIECAM02 and Beyond”. Slides from a tutorial at the IS&T/SID 12th Color Imaging Conference. 9 November 2004. Retrieved 19 September 2007.
- ^ Schanda, János (2007). Colorimetry: Understanding the CIE System. Wiley Interscience. ISBN 978-0-470-04904-4. http://books.google.com/?id=g8VDAgAACAAJ&dq=intitle:Colorimetry+intitle:Understanding+intitle:the+intitle:CIE+intitle:System, page 88.
- ^ Hunt, Robert William Gainer (1993). Leslie D. Stroebel, Richard D. Zakia. ed. The Focal Encyclopedia of Photography. Focal Press. p. 124. ISBN 0240514173. http://books.google.com/?id=CU7-2ZLGFpYC&pg=PA124&dq=%22correlate+of+saturation%22+cielab+chroma+lightness+chromaticity.
- ^ Lübbe, Eva (2010). Colours in the Mind - Colour Systems in Reality- A formula for colour saturation. [Book on Demand]. ISBN 978-3-7881-4057-1.
- ^ a b Moroney, Nathan; Fairchild, Mark D.; Hunt, Robert W.G.; Li, Changjun; Luo, M. Ronnier; Newman, Todd (November 12 2002). "The CIECAM02 Color Appearance Model" (PDF). IS&T/SID Tenth Color Imaging Conference. Scottsdale, Arizona: The Society for Imaging Science and Technology. ISBN 0-89208-241-0. http://www.polybytes.com/misc/Meet_CIECAM02.pdf.
- ^ Juan, Lu-Yin G.; Luo, Ming R. (June 2002). "Magnitude estimation for scaling saturation". In Robert Chung, Allan Rodrigues. Proceedings of SPIE. 4421. 9th Congress of the International Colour Association. pp. 575–578. doi:10.1117/12.464511. http://spiedl.aip.org/getabs/servlet/GetabsServlet?prog=normal&id=PSISDG004421000001000575000001&idtype=cvips&gifs=yes.
- ^ Stroebel, Leslie D.; Zakia, Richard D. (1993). The Focal Encyclopedia of Photography (3E ed.). Focal Press. p. 121. ISBN 0240514173. http://books.google.com/?id=CU7-2ZLGFpYC&pg=PA121&dq=%22excitation+purity%22.